Welcome to the Earth.Org Global Sustainability Index, where Earth.Org examines the policies and actions regarding the environment of every nation on earth. Combining the most respected global indexes on pollution, climate change, policy, energy, oceans, biodiversity we have produced an overall Global Index, which will be updated annually. This is the Global Sustainability Index scorecard for Germany.
In 2019, Germany emitted 805 million tons of CO2- a decrease of 35.7% compared to 1990 levels. The reason for this drop is mainly due to a drop in coal use and higher renewables-based power production. Some coal was also substituted with natural gas due to lower gas prices and rising carbon prices in the EU Emissions Trading Scheme (ETS).
While the original target of a 40% reduction in emissions below 1990 levels by 2020 was abandoned by the government, the effects of the coronavirus may help the country meet its original target after all.
However, Germany’s Climate and Energy Package, agreed in September 2019, does not contain enough policy action to meet its own emissions reduction targets. In terms of its carbon neutrality by 2050 goal, the package does not have a clear long-term vision to achieve this. Positive aspects of the package- a coal phase-out, a carbon price on fuels in buildings and transport and an overarching climate law- are also unclear and unambitious enough to meet the government’s targets, let alone those of the Paris Agreement.
The coal phase-out schedule of 2038 is too slow to meet climate objectives and a new coal-fired power station is set to go online this year. Further, the effects of the proposed carbon price- 10 euros per ton of carbon- will be minimal.
Regarding renewable energy, capacity additions of wind and solar power have slowed down significantly since the peak years of 2010-2012. However, in 2019, more than 40% of the country’s power consumption was covered by renewables, exceeding its 2020 target of 35% one year ahead. The government is now looking at 65% by 2030, as stated in its Climate Action Program.
The most effective ways for Germany to reach its targets include rolling out renewable energy, bringing down energy consumption and ending the use of fossil fuels.
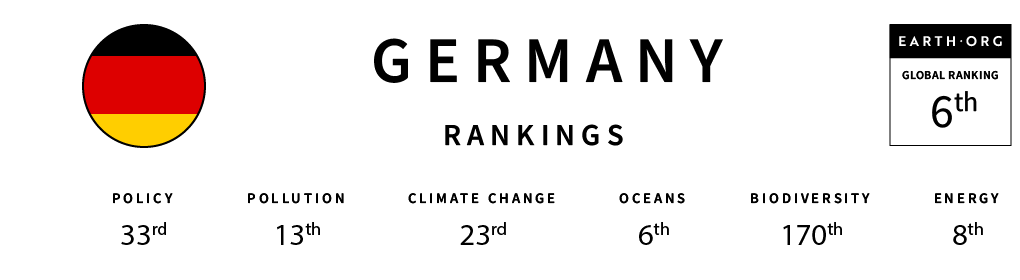
- In January, Germany agreed on plans to phase out coal-fired power generation by 2038, however a new coal plant is scheduled to go online later this year.
- In April, Germany generated a record-high 32.2 GW of social power, accounting for 40% of the country’s electricity needs.
- Germany did not submit its own Paris Agreement targets, but is part of the EU, which committed to reducing emissions by ‘at least 55%’ below 1990 levels by 2030.
- In its Climate Action Plan 2050, Germany set itself domestic reduction targets for 2020, 2030 and 2040. The previous 2020 target of at least a 40% reduction below 1990 levels is no longer pursued; the government admitted that it would not reach this target.
- The target for 2030 is 55% below 1990 levels and is under parliamentary discussion. However, the country is not on track to meet this goal. The former target of a 70% reduction by 2040 below 1990 levels has been dropped as a ‘more ambitious target will be needed’.
- The country has a long-term goal of achieving GHG neutrality by 2050, replacing an earlier goal of 80-95% reduction.
You might also like: Global Emissions (2016)
References:
-
Biodiversity, Policy: Sachs, J., Schmidt-Traub, G., Kroll, C., Lafortune, G., Fuller, G. (2019): Sustainable Development Report 2019. New York: Bertelsmann Stiftung and Sustainable Development Solutions Network (SDSN).
-
Oceans: Halpern, Benjamin S., et al. “An index to assess the health and benefits of the global ocean.” Nature 488.7413 (2012): 615-620.
-
Pollution: Wendling, Z. A., Emerson, J. W., Esty, D. C., Levy, M. A., de Sherbinin, A., et al. (2018). 2018 Environmental Performance Index. New Haven, CT: Yale Center for Environmental Law & Policy. https://epi.yale.edu/
-
Climate Change: Climate Change Performance Index; Jan Burck, Ursula Hagen, Niklas Höhne, Leonardo Nascimento, Christoph Bals, ISBN 978-3-943704-75-4, 2019
-
Energy: Enerdata –World Energy Statistics – Yearbook.
World Energy Statistics











