Climate change has led to the large-scale burning of our forests, with human, plant, and animal life being directly and indirectly affected. Forest fires are important for proper land management. However, if the fires keep raging for longer durations, encompassing more land and life with them, then they can be detrimental to the safety of our planet. We explore the impact of wildfires on the environment and biodiversity.
__
Many parts of the world have experienced one of the hottest summers on record this year, due to the increased number and intensity of heatwaves. With this rise in temperatures, forests have become more perceptible to wildfires and tend to burn more easily than in the past.
Fire has always been a natural part of our ecosystems as it is one of the five elements of nature along with air, water, soil, and space. All are quite important for our survival and to maintain a balance on our planet. However, climate change has contributed to a massive rise in extreme events – especially wildfires – most of which destroy huge areas of forests and wildlife habitats, threatening the survival of hundreds of thousands of animals.
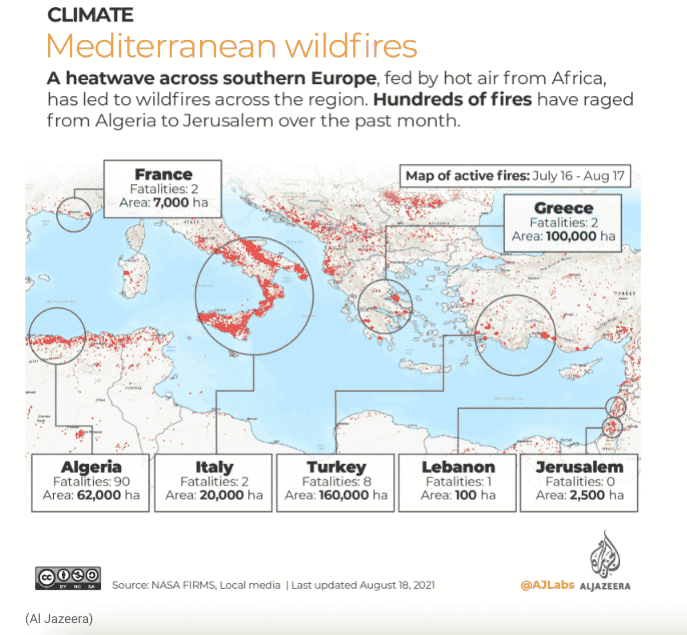
Image 1: Wildfires in the Mediterranean, 2021
One might naturally wonder how fires could be useful for survival. Before diving into that, let us understand when a wildfire or a forest fire may occur.
What Causes Wildfires?
A wildfire starts when there are combustible objects or dry fuel, there is oxygen in the air and a source to create a spark such as lightning, or human activities like campfires, arson, or cigarettes if not properly extinguished. Dry fuel such as grass, leaves, or branches – found in forests in large quantities – make it easier for the fire to grow and spread. Other factors such as dry air and strong winds can increase the chances of a fire occurring or spreading further, hence forest fires are more likely to occur during heatwaves.
Sometimes, agricultural activities such as land clearing by fire – also known as slash and burn – can also cause a forest fire. Poor farming practices are quite harmful to forests as they contribute to soil erosion, which creates the perfect conditions for a fire to occur.
Invasive and reckless human activities such as land clearing to facilitate industrial and urban expansion have also been found to be a growing cause of wildfires. Statistics show that nearly 85% of global wildfires are caused by humans and their negligence. To name another example, of the massive wildfires that broke out in Turkey in 2021, a staggering 71% were also caused by human activities.
The Impact of Wildfires: Benefits and Dangers to the Environment
Regular fires have played a fundamental role in sustaining the biodiversity of a particular region. Certain species of plant and animal life depend on fire and help in the evolution process by creating a disequilibrium that gives them new opportunities to become stronger and more resilient. Hence, fire becomes the disruptor driving the process of natural selection.
Many indigenous communities in parts of Australia, North America, and India would start controlled fires to facilitate the development of specific ecosystems. In fact, fires can reduce the accumulation of dry fuel and any other unwanted organic matter and hence prove useful for mitigating the intensity of future, non-planned fires. Controlled fires are also important for recycling nutrients, building up plants’ resilience to fires, and controlling diseases by destroying unwanted insects.
Specifically, controlled fires are valuable to woodpeckers and other birds as they get a large supply of dead wood for foraging. Fires promote the production of seeds in some specific plant species whose cones depend on fire to open and release seeds. Such fires prove to be quite important for researchers to better understand our biodiversity and the role of fires and they also provide training to firefighters.
Controlled fires may also give way to the emergence of new plant life with particularly enhanced characteristics that may not be endemic to a specific region. This way, pyro-diversity – the variation in spatio-temporal fire patterns – can be beneficial to biodiversity.
Even though in some instances, forest fires can have some positive impacts, they still tend to hurt the biodiversity within the region they occur in. One of the largest wildfire events in history is the 2019-2020 Australian bushfires, which went down in history for their catastrophic impact on wildlife. Australia has quite a great biodiversity network with many species of plants, animals, and other organisms which were destroyed or damaged during these bushfires. 12.6 million hectares of land were burned, killing about 3 billion animals and dozens of people. Many species became endangered or closer to extinction as a result. The International Union for Conservation of Nature has categorised koalas and orangutans to be at risk of extinction and changing patterns of fires worldwide are only adding on to the dangers of species loss.
You might also like: 3 Things to Know About Australia Wildfires and Bushfires

Image 2: Hectares of forests lost to wildfires, 2021
Large-scale and intense wildfires like the ones that occurred in Australia can have other indirect health impacts, due to smoke and other particulate matter, leading to respiratory issues such as asthma, bronchitis, reduced lung function, as well as skin problems, eye irritation, and in some cases even premature death.
Wildfires are also adding to the list of threats to food security and are affecting various species of crops and agricultural produce. One of the most affected industries during Australia’s 2019-2020 bushfires was the dairy industry. The states of Victoria and New South Wales – the country’s top milk-producing states – lost huge amounts of land. Fires also affected cattle, harming the production of meat, honey, and wool.
Can We Mitigate the Impact of Wildfires?
Fire activity has been changing with more frequent and more disastrous fires breaking out more and more often in fire-prone areas such as Siberia, California, and Australia. Contrarily, fires seem to be declining in areas like the grasslands of North America and Brazil, whose environments are pyro-dependent.
To mitigate the impact of wildfires, countries like the US, Brazil, Australia, Indonesia have instituted forest administrative bodies and enacted forest protection policies. Greece is the first country in the world to have set up a Climate Crisis Ministry to tackle the challenges that the changing climate poses to our planet with a policy of disaster prevention and preparedness, which Christos Styliandes, minister for Climate Crisis described as “the most effective weapon.”
Climate change is a major reason for the changing patterns of fire activity and the increased frequency of wildfires. Changing landscapes and their mismanagement can also be blamed for the increase in burning. The climate that forests adapted to is now constantly changing, making them less resilient and hence more prone to fires.
This creates a vicious loop: Wildfires are indeed further contributing to a rise in carbon dioxide released into the atmosphere. In February this year, a report by the UN stated that wildfires globally are set to double by 2100, which would hit regions that were previously unaffected by these events. There is an immediate need for more funding and efforts toward preventing wildfires rather than extinguishing them after they have already caused colossal damage.
While is impossible to prevent all wildfires from happening, mitigating climate change will play a crucial role in tackling the negative impact of wildfires.
You might also like: What Causes Wildfires?


















