Pollution, extreme weather, and natural hazards are just some examples of events caused by global warming. The US is currently experiencing some of its worst droughts and heatwaves. Water as well as air pollution are rising to unprecedented levels across the country. We explore the worst states for climate change in the US.
—
Worst States for Climate Change: Pollution
1. Water Pollution
Caused by sewage, oil spills, industrial waste, as well as plastic waste, water pollution has catastrophic effects on the marine ecosystem and it can lead to algal bloom in the marine environment, which in turn reduces oxygen levels in water. This process is known as eutrophication, which suffocates plants and animals, and harms the marine ecology. Besides, chemicals and heavy metals from wastewater are toxic to aquatic life, posing a serious threat to the food chain.
It is reported that 50% of assessed river and stream miles across the US – amounting to more than 700,000 miles of waterways – as well as 55% of lake acres and 25% of estuary miles are impaired due to pollution.
Below is a list of the country’s top 10 states with the most polluted river and stream in 2020, ranked according to the percentage of their total river and stream impaired:
- Delaware (97%)
- New Jersey (95%)
- Hawaii (91%)
- California (87%)
- Louisiana (86%)
- Oregon (86%)
- Iowa (84%)
- South Carolina (81%)
- Kansas (79%)
- South Dakota (78%)
Water pollution can also harm our health by entering our tap water system. A report published in July 2022 showed that 371 of California’s water systems – which supply water to more than 920,000 people mostly located in the Central Valley – had unsafe levels of contamination including arsenic and nitrate. Its negative impacts on human health include liver and kidney failure as well as cancer. In fact, thousands of people in the United States get sick every year from Legionnaires’ disease, a severe form of pneumonia contracted from water sources such as piped water.
Below are the 10 states in the US with the worst tap water in 2020:
- Washington
- California
- Arizona
- Florida
- New Jersey
- Pennsylvania
- Georgia
- Puerto Rico
- Texas
- Ohio
You might also like: Tainted California’s Water Poses Health Risks for 1 Million in State: Report
2. Air Pollution
Air pollution is mainly caused by the burning of fossil fuels, wildfires, ozone and smog. It is detrimental not only to the environment, but also to our health, and may referred to it as “a silent public health emergency”. About 68 million tons of air pollution were emitted into the atmosphere in the US in 2020 alone. In addition, 4 in 10 individuals in the country – accounting for about 135 million people – are currently living in areas with unhealthy and polluted air.
Unfortunately, the situation is expected to further worsen in coming years due to climate change, as large-scale wildfires, which are becoming increasingly frequent as a result of global warming, release carbon emissions, smog and pollutants into the air.
Below listed the 15 most polluted cities in the country for particulate matter (PM 2.5) levels according to the country’s 2022 State of the Air report.
- Visalia, California (annual PM2.5 of 16.6 μg/m3)
- Fresno-Madera-Hanford, California (annual PM2.5 of 16.6 μg/m3)
- San Jose-San Francisco-Oakland, California (annual PM2.5 of 14.5 μg/m3)
- Los Angeles-Long Beach, California (annual PM2.5 of 14.2 μg/m3)
- Medford-Grants Pass, Oregon (annual PM2.5 of 13.9 μg/m3)
- Fairbanks, Alaska (annual PM2.5 of 13 μg/m3)
- Phoenix-Mesa, Arizona (annual PM2.5 of 12.8 μg/m3)
- Chico, California (annual PM2.5 of 12.2 μg/m3)
- El Centro, California (annual PM2.5 of 12.1 μg/m3)
You might also like: 15 Most Polluted Cities in the US
Worst States for Climate Change: Extreme Weather
Extreme weather is ultimately prompted by climate change. As the average global temperature rises, the water cycle speeds up with an increase in evaporation rate from soil and transpiration from plants, influencing the precipitation pattern. It is found that some historically wet areas are likely to experience an increase in precipitation, accompanied by an increased risk of flooding, while historically dry areas are likely to experience less precipitation with a higher risk of droughts and wildfires.
3. Heatwaves
A heatwave is a period of higher than average temperatures in a particular region, usually lasting for a few days.
Global warming has caused heatwaves to be increasingly longer, more intense, and more frequent in recent years. An average of two heatwaves per year was observed in the US during the 1960s. The number increased steadily and it currently sits at around six heatwaves yearly. Of the 50 metropolitan areas in the indicator by the United States Environmental Protection Agency, 17 of them experienced an increase in heatwave intensity between the 1960s and 2020s.
Prolonged exposure to excessive heat can also damage crops and affect livestock and can raise the risk of wildfires, which not only threaten the ecosystem but also humans. About 65.2 million people — 20% of the US population — live in the areas expected to have dangerous levels of heat and hundreds of people die as a result of extreme temperatures every year in the country.
Here are the five cities that have a record-breaking heatwave that hit the country in June 2022:
- Paducah, Kentucky (97°F)
- Evansville, Indiana (98°F)
- Cape Girardeau, Missouri (100°F)
- Poplar Bluff, Missouri (100°F)
- Carbondale, Illinois (99°F)
You might also like: Water Shortage in Texas
4. Tropical Cyclones
Tropical cyclones – which can be categorised as hurricanes, tropical depression, and tropical storms – are rotating, organised systems of clouds and thunderstorms that originate over tropical or subtropical waters.
Over the past 50 years, tropical cyclones had cost the country a staggering US$1,407.6 billion, equivalent to an average of $78 million loss every day. They have also caused nearly 880,000 casualties, an average of 43 deaths a day.
Due to climate change, tropical cyclones are becoming progressively more devastating, resulting in even more economic and human losses. These extreme weather events are expected to be more frequent, more intense with higher wind speeds, and have heavier rains, as the increase in sea surface temperatures provides them more energy.
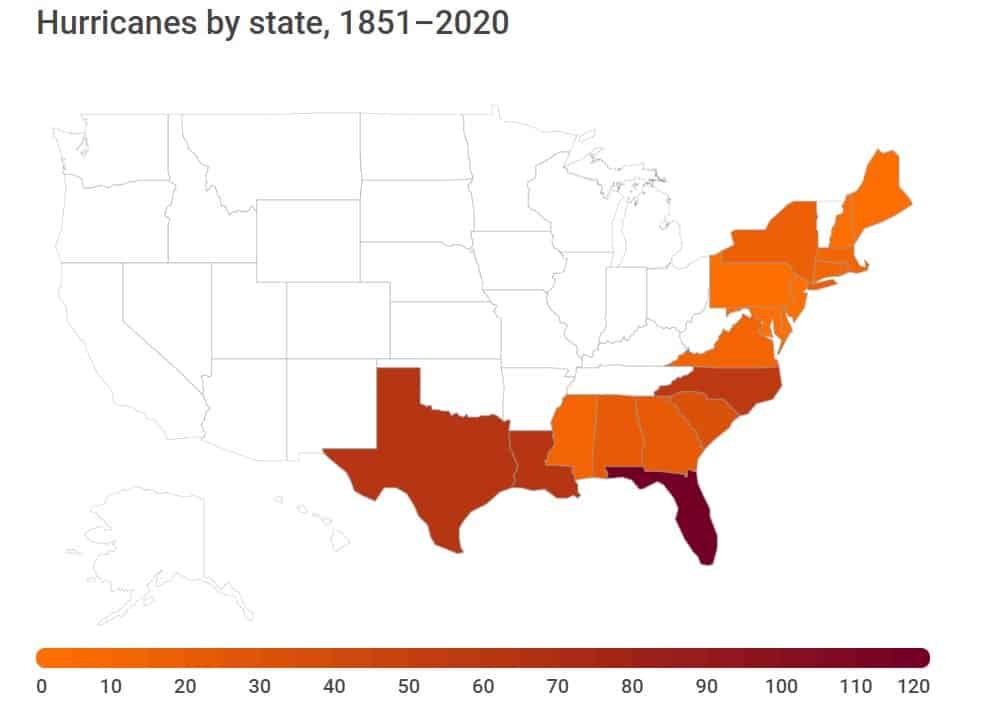
States that are subject to topical cyclones should therefore be more cautious and plan investments to ramp up their resilience and preventive measures. Below are the states that experienced the most hurricanes between 1851 and 2020
- Florida (120 hurricanes)
- Texas (64 hurricanes)
- Louisiana (62 hurricanes)
- North Carolina (58 hurricanes)
- South Carolina (31 hurricanes)
- Alabama (23 hurricanes)
- Georgia (21 hurricanes)
- New York (15 hurricanes)
- Mississippi (14 hurricanes)
- Virginia (13 hurricanes)
Worst States for Climate Change: Natural Hazards
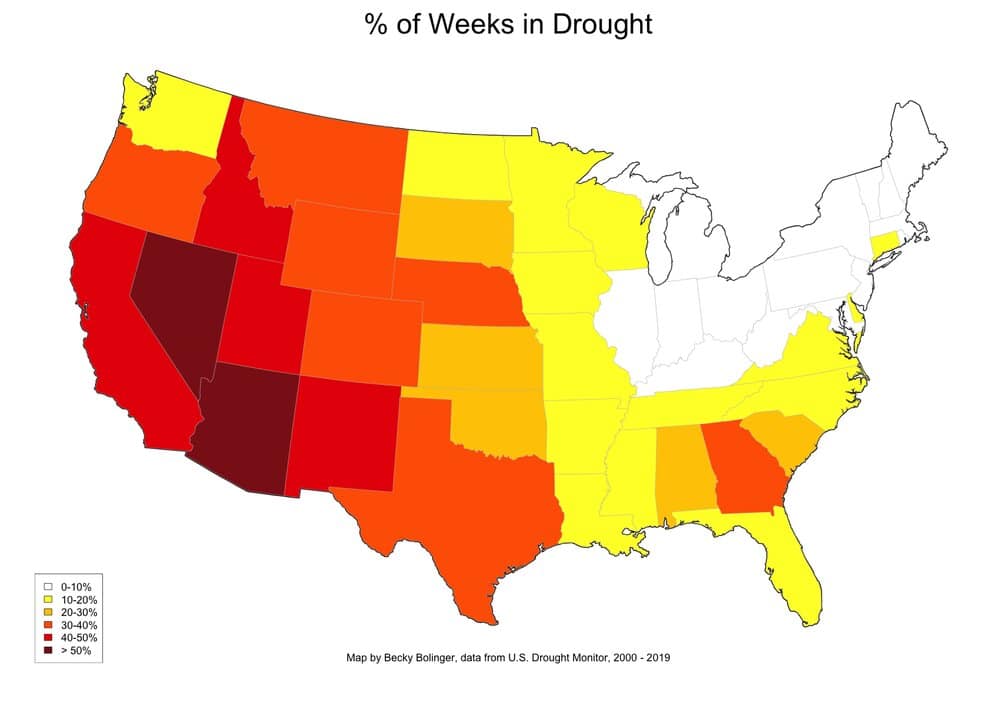
5. Droughts
Drought refers to the extended imbalance between precipitation and evaporation, which lead to a prolonged period of dry weather, often resulting in serious water shortage.
Droughts in the US have catastrophic impacts. With each drought, the country experiences an estimated USD$9.6 billion economic loss. The agriculture sector inevitably bears the brunt, dealing with a decrease in productivity of the farmland. 229 million acres of crops were found to be undergoing drought conditions in July 2022.
As of September 2021, 88% of the population in California lived in drought, with nearly 50% in exceptional drought areas, experiencing the most intense kind of drought. With global warming, droughts are expected to become even more frequent and intense in the coming years.
You might also like: California Still In A Drought: 3 Years and Counting
Here are the 5 states that most frequently encounter exceptional drought:
- California
- Colorado
- New Mexico
- Oklahoma
- Texas
6. Wildfires
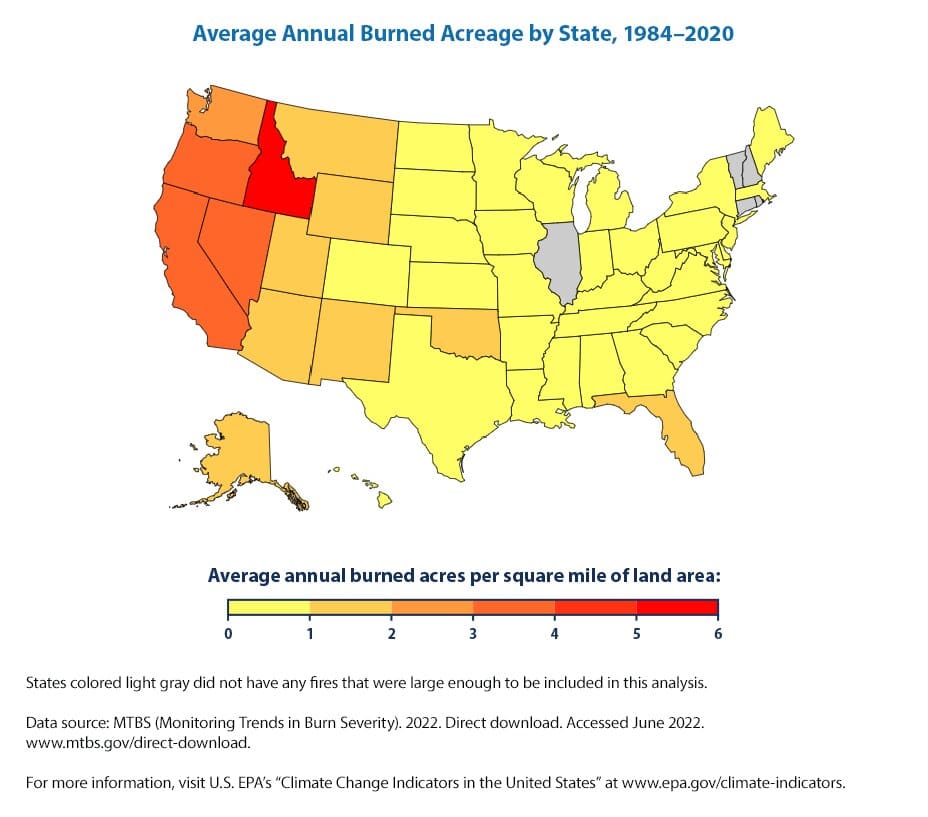
Similar to drought, wildfires have become much more concerning with climate change. Hotter temperatures cause severe heatwaves and longer droughts. These increase the amount of dry vegetation, which exacerbates the risk of more intense and destructive fires developing.
In the US, a typical fire season used to last for four months. Now, fire seasons usually last up to eight months. In 2020, the US experienced one of the largest wildfires in history, which lasted for the entire year, tearing through parts of California, Oregon and Washington state.
Wildfires impact both humans and the environment. A public health crisis is always the imminent and pressing result. Suffocating smoke is especially harmful, if not fatal, to people with pre-existing respiratory diseases. Forests, home to millions of valuable species and also important to the ecosystem, perished after wildfires. Over the past two years, over 10,000 sequoia trees in California were destroyed by wildfires.
Below listed the top 10 states with the highest total number of acres burned by wildfire in 2021:
- California (2,233,666 acres)
- Oregon (828,777 acres)
- Montana (747,678 acres)
- Washington (674,222 acres)
- Arizona (524,428 acres)
- Idaho (439,600 acres)
- Alaska (253,357 acres)
- Texas (168,258 acres)
- Kansas (163,982 acres)
- New Mexico (123,792 acres)
You might also like: 15 Largest Wildfires in US History
7. Floods
A flood is the accumulation of water over dry land, which can be caused by the overflow of inland waters such as rivers and streams, or by an unusual accumulation of water from sources such as heavy rains. Floods are the most common and among the most deadly natural hazards in the US. It is estimated that 41 million US residents are at risk from river flooding, while 8.6 million are at risk from coastal flooding, which result in more than 100 fatalities annually.
Intense precipitation, hurricanes, and rainstorms triggered by climate change result in easier overflow of rivers and accumulation of waters, leading to more flooding. The floodplains in the US are expected to grow by approximately 45% by the century’s end, while coastal flooding are estimated to double within a decade. The Mississippi River Valley, Midwest and Northeast United States will be much more prone to flooding in the future.
Here are the states with the highest risk of flooding, ranked according to the percentage of the state within flood hazard areas:
- Louisiana (50.56%)
- Florida (40.08%)
- Mississippi (23.14%)
- Arkansas (22.57%)
- New Jersey (19.27%)
- South Carolina (19.2%)
- Maryland (19.17%)
- Delaware (19.12%)
- District Columbia (17.71%)
- North Carolina (17.13%)
You might also like: Sea Level Rise Projections: Top 10 Cities at Risk of Flooding
Future Outlook
To counter climate change, the US has set to reduce net greenhouse gas emissions by 50-52% below 2005 levels by 2030, and pledged to reach net-zero emission by 2050.
The government plans to invested nearly US$1 billion in Climate-Smart Agriculture, producing commodities that use climate-smart practices. Regulations will be re-established to protect America’s waterways, ensuring environmental protections for water bodies that are critical to the health, safety and economic vitality of communities. On an international level, President Biden worked with EU counterparts to rally more than 100 countries to join the Global Methane Pledge, a new partnership to reduce super-polluting methane emissions 30% from 2020 levels by 2030.
The US Methane Emissions Reduction Action Plan was also issued, with more than 40 actions across multiple agencies pledging to cut methane emissions from the oil and gas sector, agriculture, buildings, and more.
Only with continuous and substantial efforts not only from the government but also from companies and individuals, the country can hope to reach its climate targets.
If you enjoyed this article on the worst states for climate change in the US, you might also like: Best Places to Live to Avoid Climate Change
This story is funded by readers like you
Our non-profit newsroom provides climate coverage free of charge and advertising. Your one-off or monthly donations play a crucial role in supporting our operations, expanding our reach, and maintaining our editorial independence.
About EO | Mission Statement | Impact & Reach | Write for us


















